Shot Types & Filming Scenarios
Learn About Different Shot Types and Which Is Best For Each Filming Scenario
Shot Types and Shot Framing Explained
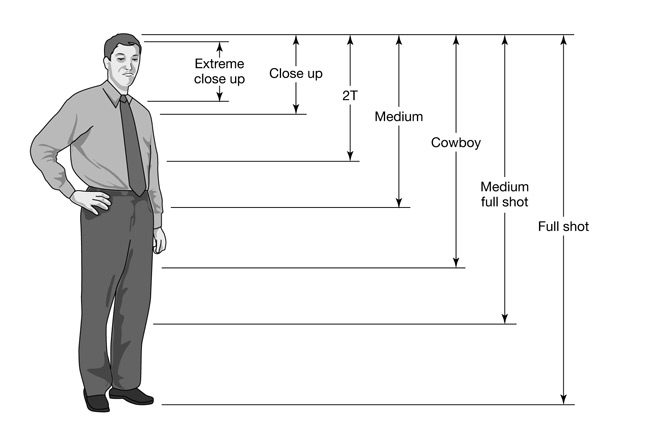
The following shot types are referred to in terms relative to the subject.
The point isn’t to necessarily memorize the names of all of these shots, but rather to better understand the purpose of each shot type in regards to composing an image.
Instead of just “pointing the camera” at something, composing a great shot requires that you frame it properly based on the desired effect.
The subject in all of the following shots is a boy standing in front of a house.
EWS (Extreme Wide Shot)
In the EWS, the view is so far from the subject that he isn’t even visible. The point of this shot is to show the subject’s surroundings. This is often used as an establishing shot to help show the audience where the action is taking place.

VWS (Very Wide Shot)
The VWS is much closer to the subject. He is (just) visible here, but the emphasis is still on placing him in his environment. This also works as an establishing shot.

WS (Wide Shot)
In the WS, the subject takes up the full frame or as much of it as is comfortably possible. In this case, the boy’s feet are almost at the bottom of frame, and his head is almost at the top.
The small amount of room above and below the subject can be thought of as safety room — you don’t want to be cutting the top of the head off.
This shot is also known as a “long shot” or “full shot.”

MS (MidShot)
The MS shows some part of the subject in more detail while still giving an impression of the whole subject. This is about how you would see a person “in real life” if you were having a casual conversation. 
MCU (Medium Close Up)
Half way between a MS and a CU. This shot shows the face more clearly, without getting uncomfortably close.
This is a great shot for most talking videos on YouTube.

CU (Close Up)
A certain feature or part of the subject takes up the whole frame.

ECU (Extreme Close Up)
The ECU gets right in and shows extreme detail. For people, the ECU is used to convey emotion.
CA (Cutaway)
A cutaway is a shot that’s usually of something other than the current action. It could be a different subject (e.g. these children), a CU of a different part of the subject (e.g. a CU of the subject’s hands), or just about anything else.
The CA is used as a “buffer” between shots (to help the editing process), or to add interest/information.

Cut-In
Shows some (other) part of the subject in detail.

Two-Shot
A shot of two people, framed similarly to a mid shot.

OSS (Over The Shoulder Shot)
Looking from behind a person at the subject. These are great shots to get for conversational scenes, but they typically require a camera person to capture.

Noddy Shot
Usually refers to a shot of the interviewer listening and reacting to the subject. These shots are also great for YouTube.

POV (Point Of View)
Shows a view from the subject’s perspective.
Weather Shot
The subject is the weather. Can be used for other purposes, e.g. background for graphics.

Cowboy Shot
Used commonly in old Western movies to show the gun belts of cowboys, this can also be an interesting way to frame a shot of the subject to show more of their body and/or outfit.

These images were sourced from http://www.mediacollege.com/ – Check it out for more information or to dive deeper into film theory.
